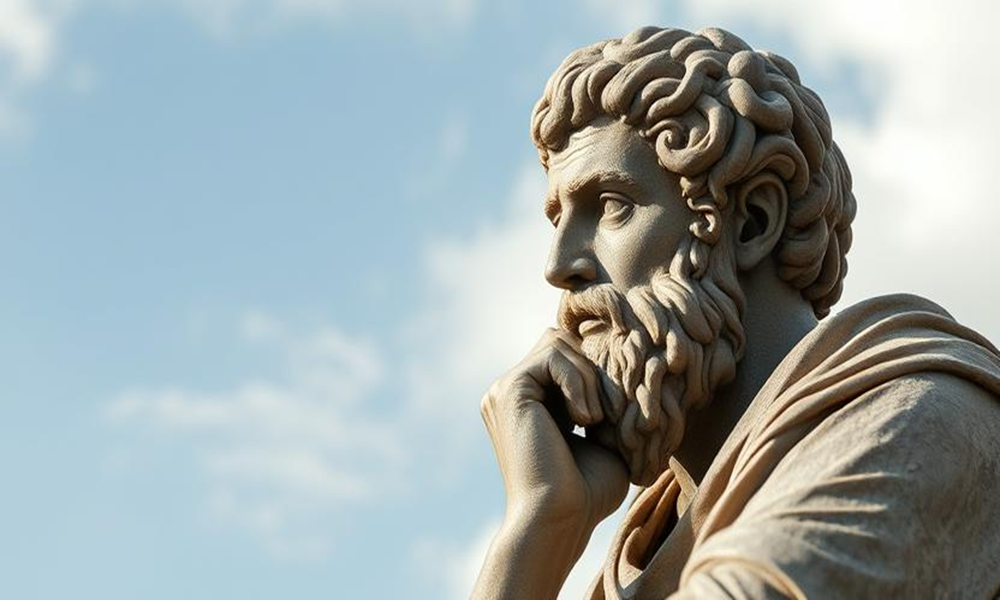
Thinker Aristotle remains one of history’s most influential philosophers. His contributions span ethics, politics, metaphysics, and science. Born in ancient Greece, his works continue to guide scholars today.
Aristotle studied under Plato and later taught Alexander the Great. His ideas shaped Western thought for centuries. He introduced logic as a system of reasoning. His ethical theories still influence modern philosophy.
The Life of Thinker Aristotle
Early Years and Education
Aristotle was born in 384 BCE in Stagira, a city in ancient Greece. His father was a physician, which sparked his interest in science. At 17, he enrolled in Plato’s Academy in Athens.
For 20 years, he studied under Plato, developing his own ideas. Unlike Plato, Aristotle believed in empirical observation. He emphasized studying the natural world to gain knowledge.
After Plato’s death, Aristotle left Athens. He later served as a tutor to Alexander the Great. This role gave him access to vast knowledge and resources.
Establishing the Lyceum
In 335 BCE, Aristotle established the Lyceum in Athens. It became a center for research and education. He developed systematic methods for studying different subjects.
The Lyceum welcomed students from all backgrounds. Aristotle’s teachings covered philosophy, biology, politics, and ethics. His approach emphasized critical thinking and inquiry.
Thinker Aristotle and His Philosophical Contributions
Logic and Reasoning
Aristotle contributed to many fields, including logic, ethics, and politics. His works laid the foundation for modern science and philosophy.
He developed the system of deductive reasoning. His work, Organon, outlines principles of logical thinking. This system helped scholars understand argument structures.
His logical principles remain essential in philosophy, mathematics, and computer science. The use of syllogisms is still common in critical thinking.
Ethics and the Concept of Virtue
His ethical philosophy focuses on achieving eudaimonia, or human flourishing. He believed virtue is the path to happiness. This idea influences contemporary ethical theories.
Aristotle’s Nicomachean Ethics explores the importance of moral character. He introduced the concept of the Golden Mean, which suggests moderation in all aspects of life.
Metaphysics and the Study of Existence
Aristotle explored metaphysics, examining existence and reality. His ideas shaped later philosophical and theological discussions.
He proposed that everything has a purpose and potential, which he called telos. This concept influenced medieval scholars and theologians.
Aristotle’s Influence on Science and Logic
Contributions to Natural Sciences
Aristotle’s scientific method emphasized observation and classification. He studied biology, physics, and astronomy. His classifications of animals remained relevant for centuries.
Thinker Aristotle work in biology included detailed studies of anatomy and reproduction. His observations on nature laid the groundwork for modern biology.
The Foundation of Logic
In logic, he introduced syllogism, a method of reasoning still used today. His logical principles helped develop modern scientific inquiry.
Thinker Aristotle approach to logic influenced later philosophers, including medieval and Renaissance thinkers. His methods remain fundamental in philosophical studies.
Aristotle’s Political Philosophy
The Ideal Government
Aristotle’s political theories focused on governance and citizenship. His book Politics examines different forms of government. He analyzed monarchy, aristocracy, and democracy.
He believed a balanced government was best. His ideas influenced political thought in ancient and modern times. He emphasized the role of education in shaping good citizens.
The Role of Citizenship
Aristotle believed that active citizenship was essential for a stable society. He argued that individuals must participate in governance to maintain a just state.
His political theories continue to shape democratic ideals. Many modern governments reflect his principles of justice and civic responsibility.
Aristotle’s Influence on Future Generations
Influence on Medieval and Renaissance Thought
Aristotle’s influence extends beyond philosophy. His ideas shaped medieval scholarship and Renaissance thought. His works were preserved by Islamic scholars and later reintroduced to Europe.
During the Middle Ages, his philosophy was integrated into Christian theology. Thinkers like Thomas Aquinas adapted his ideas to fit religious doctrine.
Impact on Modern Philosophy and Science
His teachings continue to guide modern debates in ethics, science, and politics. Universities still study his writings, and his principles remain foundational.
His work bridges ancient and modern knowledge. His methods of observation and reasoning continue to inspire scholars.
The Lasting Legacy of Thinker Aristotle
Contributions to Education and Thought
Aristotle’s impact on education remains profound. His emphasis on empirical research and logical analysis shaped academic disciplines.
His writings form the foundation of many university courses. Thinker Aristotle influence is evident in philosophy, political science, and natural sciences.
Timeless Wisdom
His emphasis on logic, ethics, and observation endures. The world still learns from his wisdom. Aristotle’s influence proves timeless, making him a cornerstone of intellectual history.
Conclusion
Thinker Aristotle revolutionized philosophy, science, and politics. His teachings shaped Western intellectual traditions. His contributions remain essential to modern education and thought.
Thinker Aristotle philosophical inquiries still inspire scholars worldwide. His methods of reasoning and observation continue to be relevant. Aristotle’s legacy proves that his ideas are truly timeless.