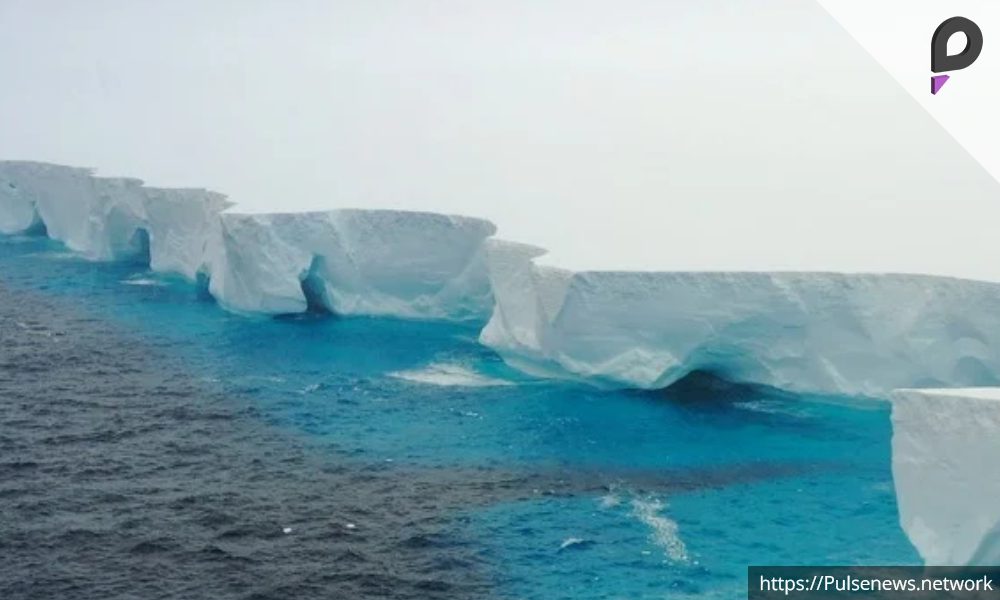
Tbilisi: A23a, the largest iceberg globally, is drifting toward South Georgia, sparking concerns for the island’s ecosystem.
The iceberg was once anchored near an underwater mountain but now follows ocean currents toward South Georgia.
Uncertain Trajectory and Potential Dangers
The iceberg is currently swirling in an ocean current bend, delaying direct movement toward the island, experts say.
Andrew Meijers, a British Antarctic Survey scientist, notes the iceberg will likely shift toward the island soon.
Simon Wallace, a South Georgia ship captain, highlights the risks if A23a fragments into smaller, hazardous ice pieces.
“Smaller chunks are harder to detect but remain dangerous, potentially blocking access to bays and fjords,” he added.
World"s largest iceberg heading for British territory | BBC News
The world"s largest iceberg is on a collision course with a remote British island, potentially putting penguins and seals in danger. The iceberg is spinning northwards from Antarctica towards South Georgia, a rugged British territory and wildlife haven, where it could ground and smash into pieces.
Measuring the Enormity of A23a
The iceberg spans approximately 3,672 square kilometers, similar to Rhode Island but twice the size of London.
After calving from the Filchner-Ronne ice shelf in 1986, it stayed grounded in the Weddell Sea for three decades.
Eventually, it shrank enough to detach and moved with currents until becoming lodged near another underwater mountain.
Impact on Wildlife and Shipping Risks
A23a’s size and position could block access to crucial feeding grounds for wildlife, including seals and penguins.
If grounded on the South Georgia shelf, it may disrupt marine biodiversity and increase risks for fishing and shipping.
Mark Belchier, the local fisheries director, warns icebergs like A23a can cause significant issues for regional navigation.
Long-term Effects and Climate Concerns
Though scientists attribute A23a’s formation to natural processes, Antarctic warming trends are a growing global concern.
Higher temperatures contribute to glacier and iceberg instability, potentially worsening sea level rises worldwide.
For now, A23a’s fate hinges on whether it drifts into open waters or stalls near South Georgia.
Satellite imagery reveals A23a remains structurally intact, defying earlier predictions of fragmenting in warmer waters.
South Georgia and nearby Marine Protected Areas could face transient but significant effects from the iceberg’s presence.